Surface Curvatures#
Functionality#
This node calculates several types of information about surface curvature:
Principal curvature values
Principal curvature directions
Gauss curvature
Mean curvature
Matrix based on principal curvature directions and surface normal.
You can refer to Wikipedia for more detailed information about these terms.
If you need only Gaussian curvature value, you can as well use simpler “Surface Gauss Curvature” node.
Inputs#
This node has the following inputs:
Surface. The surface to analyze. This input is mandatory.
U, V. Values of U and V surface parameters. These inputs are available only when Input mode parameter isset to Separate. The default value is 0.5.
UVPoints. Points at which the surface is to be analyzed. Only two of three coordinates will be used; the coordinates used are defined by the Orientation parameter. This input is available and mandatory if the Input mode parameter is set to Vertices.
Parameters#
This node has the following parameters:
Input mode. The available options are:
Separate. The values of U and V surface parameters will be provided in U and V inputs, correspondingly.
Vertices. The values of U and V surface parameters will be provided in Vertices input; only two of three coordinates of the input vertices will be used.
The default mode is Separate.
Input orientation. This parameter is available only when Input mode parameter is set to Vertices. This defines which coordinates of vertices provided in the Vertices input will be used. The available options are XY, YZ and XZ. For example, if this is set to XY, then the X coordinate of vertices will be used as surface U parameter, and Y coordinate will be used as V parameter. The default value is XY.
Clamp. This defines how the node will process the values of surface U and V parameters which are out of the surface’s domain. The available options are:
As is. Do not do anything special, just pass the parameters to the surface calculation algorithm as they are. The behaviour of the surface when the values of parameters provided are out of domain depends on specific surface: some will just calculate points by the same formula, others will give an error.
Clamp. Restrict the parameter values to the surface domain: replace values that are greater than the higher bound with higher bound value, replace values that are smaller than the lower bound with the lower bound value. For example, if the surface domain along U direction is [0 .. 1], and the value of U parameter is 1.05, calculate the point of the surface at U = 1.0.
Wrap. Wrap the parameter values to be within the surface domain, i.e. take the values modulo domain. For example, if the surface domain along U direction is [0 .. 1], and the value of U parameter is 1.05, evaluate the surface at U = 0.05.
The default mode is As is.
Sort curvatures. If checked, then the node will always make sure that curvature values are calculated so that Curvature1 value is less than Curvature2. If not checked, this will not be guaranteed. For many simple surfaces, the order of curvature values calculated without this parameter is always the same. Checked by default.
Outputs#
This node has the following outputs:
Curvature1. The first principal curvature value. If Sort curvatures parameter is checked, then this will be always the smaller principal curvature value.
Curvature2. The second principal curvature value. If Sort curvatures parameter is checked, then this will be always the bigger principal curvature value.
Dir1. The first principal curvature direction - one which corresponds to Curvature1.
Dir2. The second principal curvature direction - one which corresponds to Curvature2.
Gauss. Gauss curvature value.
Mean. Mean curvature value.
Matrix. A matrix composed from principal curvature directions. It’s X axis is looking along Dir1, Y axis is looking along Dir2 and Z axis is looking along the surface’s normal.
Examples of usage#
Use first principal curvature value for vertex colors:
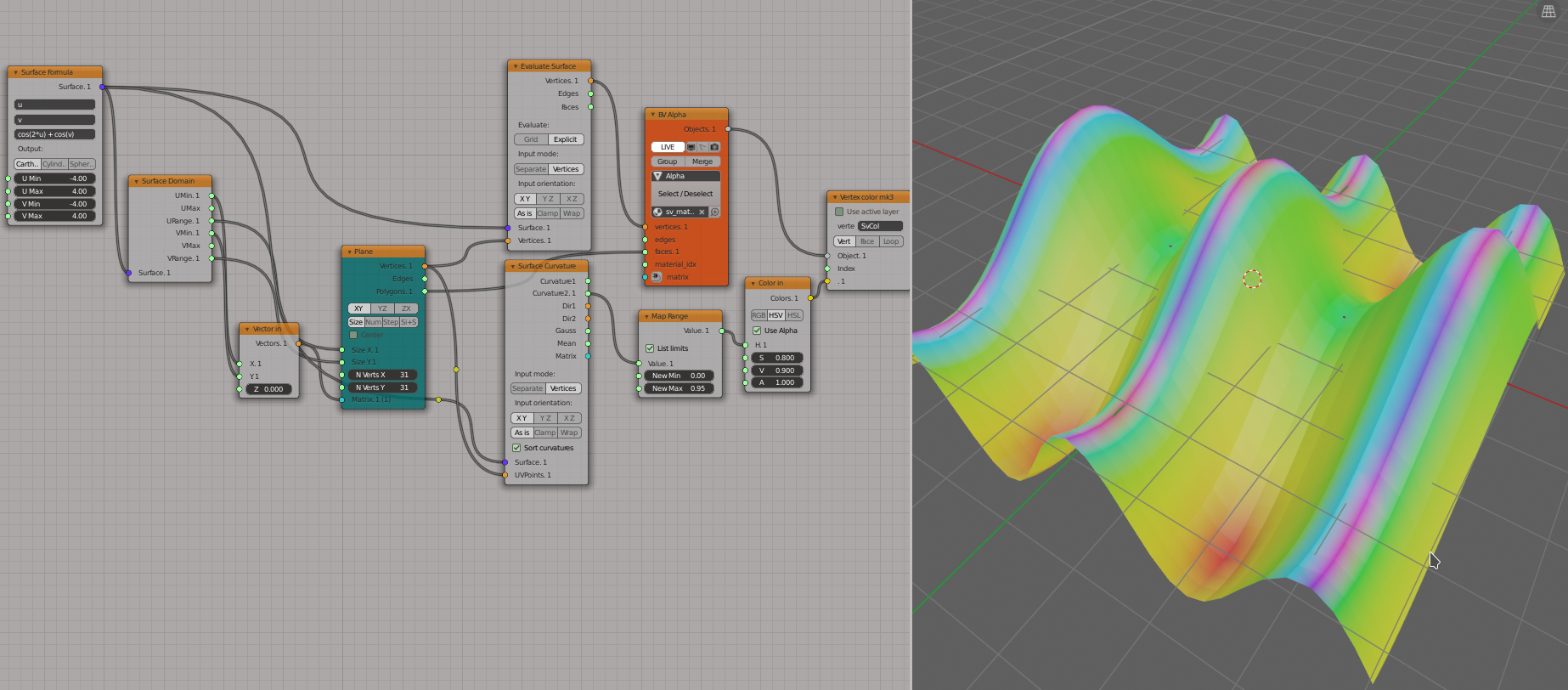
Generator-> Plane
Surfaces-> Surface Formula
Surfaces-> Surface Domain
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Number-> Map Range
Vector-> Vector In
Color-> Color In
BV Alpha: Viz-> Mesh Viewer
BPY Data->Vertex color mk3
The same with second principal curvature value:

Generator-> Plane
Surfaces-> Surface Formula
Surfaces-> Surface Domain
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Number-> Map Range
Vector-> Vector In
Color-> Color In
BV Alpha: Viz-> Mesh Viewer
BPY Data->Vertex color mk3
Gaussian curvature:

Generator-> Plane
Surfaces-> Surface Formula
Surfaces-> Surface Domain
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Number-> Map Range
Vector-> Vector In
Color-> Color In
BV Alpha: Viz-> Mesh Viewer
BPY Data->Vertex color mk3
Use Matrix output to place Suzannes on the surface:

Generator-> Suzanne
Transform-> Scale
Surfaces-> Surface Formula
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Number-> Number Range
Viz-> Viewer Draw
Here Suzannes are looking along the second principal curvature direction.
Use Matrix output to place cubes on the surface:

Generator-> Box
Generator-> Plane
Surfaces-> Surface Formula
Surfaces-> Surface Domain
Vector-> Vector In
Viz-> Viewer Draw