Minimal Surface#
Dependencies#
This node requires SciPy library to work.
Functionality#
This node generates a Surface, based on provided points, by use of RBF method. Depending on node parameters, the curve can be either interpolating (go through all points) or only approximating.
The generated surface is not, strictly speaking, guaranteed to be minimal; but in many simple cases it is close enough to the minimal.
This node, in general, searches for a surface as a mapping from (U, V) coordinates to (X, Y, Z). In many simple cases, you will want to provide just a list of points, and tell the node to use their X and Y coordinates as U and V. So, the node will actually only have to find a function which maps (X, Y) to Z. In other cases, you will want to provide a set of (X, Y, Z) points and a set of corresponding (U, V) coordinate pairs.
Inputs#
This node has the following inputs:
Vertices. The points to build minimal surface for. This input is mandatory.
Epsilon. Epsilon parameter of used RBF function; it affects the shape of generated surface. The default value is 1.0.
Smooth. Smoothness parameter of used RBF function. If this is zero, then the surface will go through all provided points; otherwise, it will be only an approximating surface. The default value is 0.0.
SrcU, SrcV. U and V coordinates for the points specified in the Vertices input. These inputs are available and mandatory if the Surface type is set to UV -> XYZ, and Explicit source UV parameter is checked.
Generator-> Plane
Vector-> Vector Noise
A*SCALAR: Number-> Scalar Math
Add: Vector-> Vector Math
Vector-> Vector Out
Matrix-> Matrix In
Viz-> Viewer Draw
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
SrcU, SrcV: XY->Z
SrcU, SrcV: YZ->X
SrcU, SrcV: ZX->Y
SrcU, SrcV: PHI,Z->XYZ
Generator-> Cylinder
Vector-> Vector Polar Input
Vector-> Vector Polar Output
Vector-> Vector Noise
A*SCALAR, ADD: Vector-> Vector Math
Matrix-> Matrix In
Viz-> Viewer Draw
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Matrix. Matrix used to extract U and V coordinates out of XYZ points. This input is available only if the Surface type is set to XY -> Z. The default is identity matrix.
Generator-> Plane
Vector-> Vector Noise
A*SCALAR, ADD: Vector-> Vector Math
Matrix-> Matrix In
Viz-> Viewer Draw
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Align surface with object:
Generator-> Plane
Vector-> Vector Noise
A*SCALAR, ADD: Vector-> Vector Math
Matrix-> Matrix In
Viz-> Viewer Draw
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Parameters#
This node has the following parameters:
Surface type. This defines which type of function the node will try to find. The available values are:
XY -> Z. The node will search for a function, mapping (X, Y) coordinates to Z (or (X, Z) to Y, or (Y, Z) to X,depending on Orientation parameter). So, in this mode the node can generate only surfaces which have a single Z value for each pair of X and Y. X, Y, Z coordinates can be rotated according to the Matrix input.
UV -> XYZ. The node will search for a function, mapping arbitrary (U, V) coordinates to (X, Y, Z). This mode is more general, but requires to pass U and V coordinate for each point somehow.
The default option is XY -> Z.
Orientation. This parameter is available only if Surface type parameter is set to XY -> Z. This defines which axis will be used as “function value”. Other two axes will be used as U and V parameters. The available values are X, Y and Z. The default option is Z.
Explicit source UV. This parameter is available only if Surface type parameter is set to UV -> XYZ. This defines whether you want to define U and V parameters for each point in the Vertices input explicitly. If checked, then U and V parameters are expected in SrcU, SrcV inputs. Otherwise, the Vertices input will expect a list of lists of points for each surface, and the node will try to guess U and V coordinates automatically. Checked by default.
Function. The specific function used by the node. The available values are:
Multi Quadric
Inverse
Gaussian
Cubic
Quintic
Thin Plate
The default function is Multi Quadric. Scipy RBF Functions
Outputs#
This node has the following output:
Surface. The generated Surface object.
Examples of usage#
Simple example of XY -> Z mode usage:
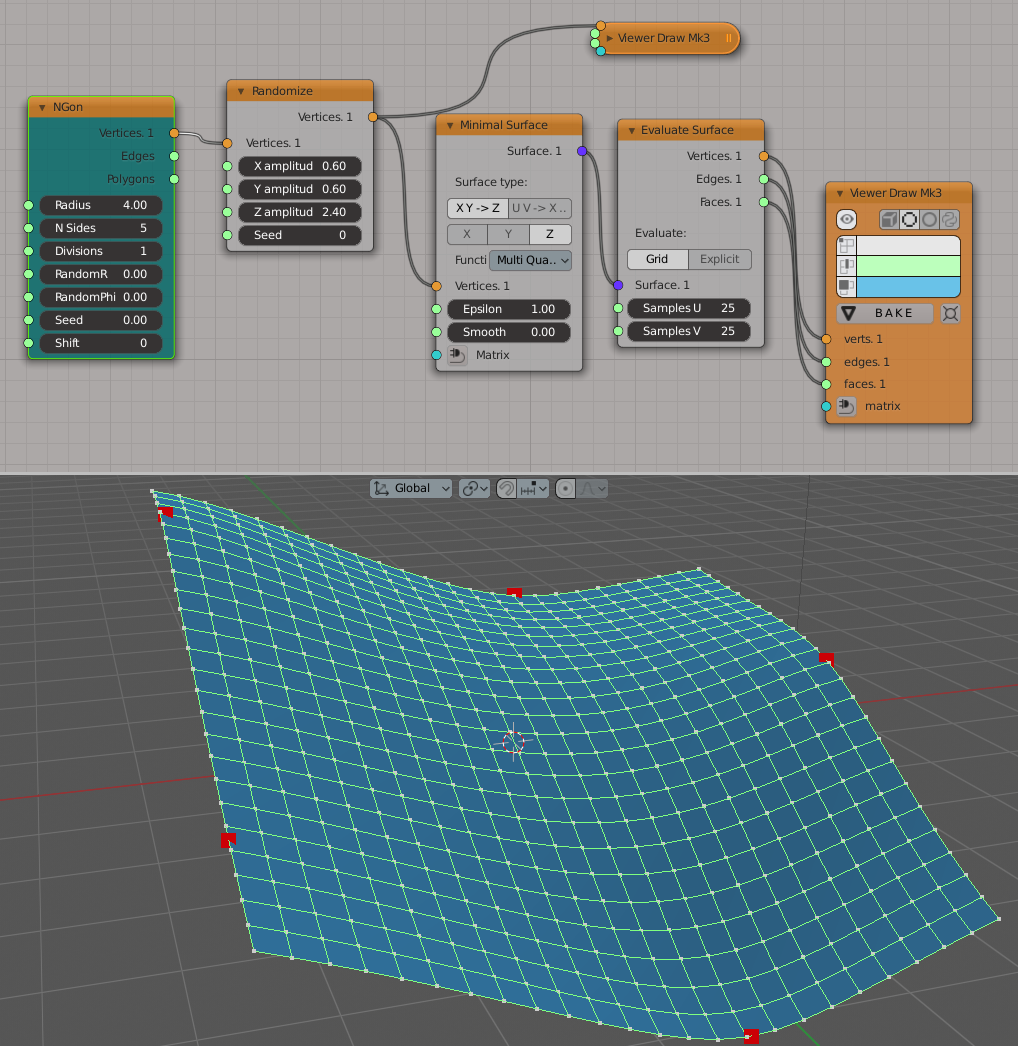
Generator-> NGon
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Transform-> Randomize
Viz-> Viewer Draw
An example of Matrix input usage; rotated and deformed plane is used as input:
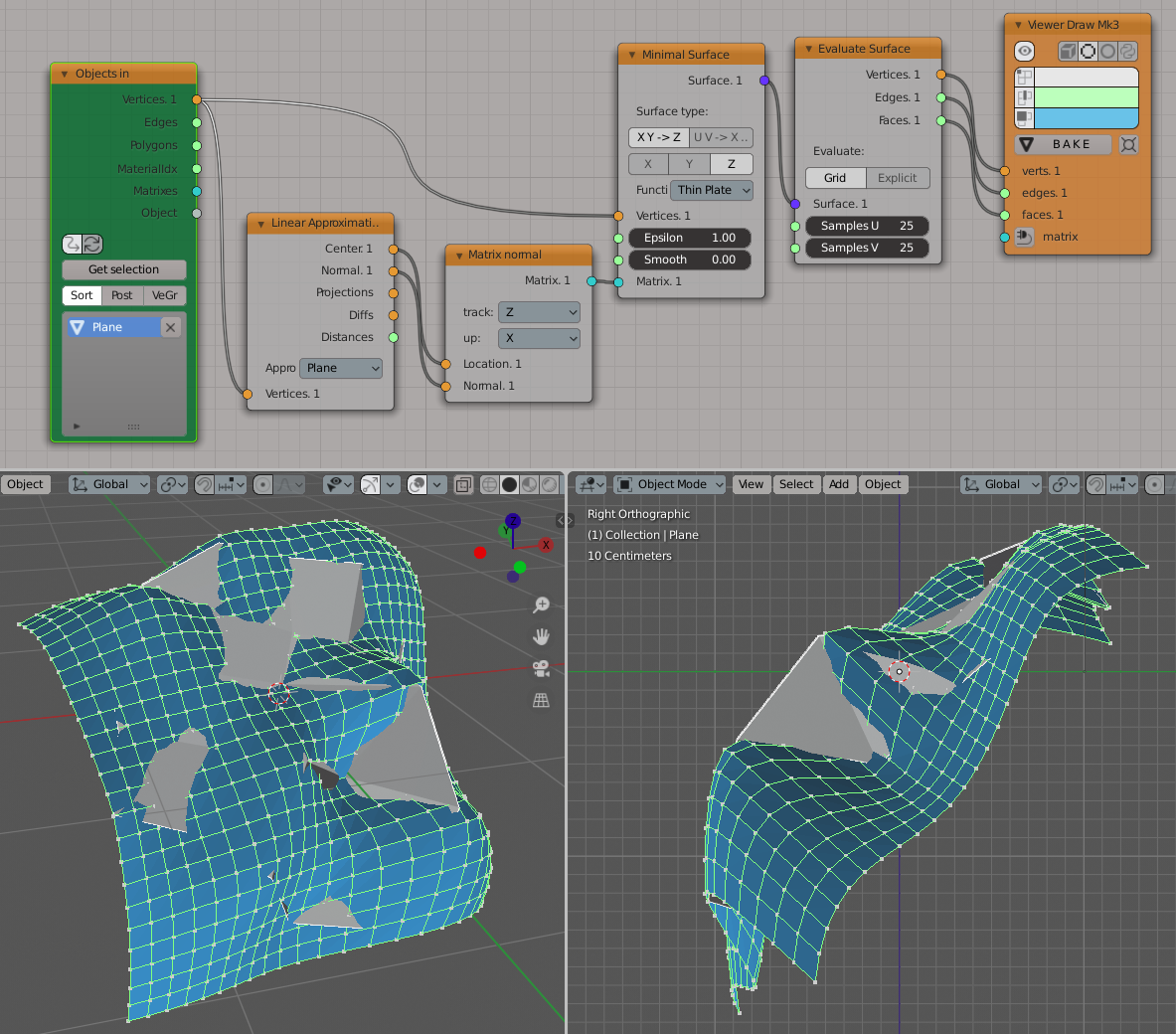
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Matrix-> Matrix Normal
Analyzers-> Linear Approximation
Viz-> Viewer Draw
Scene-> Objects In Lite
An example where UV -> XYZ mode is required to build a proper surface:
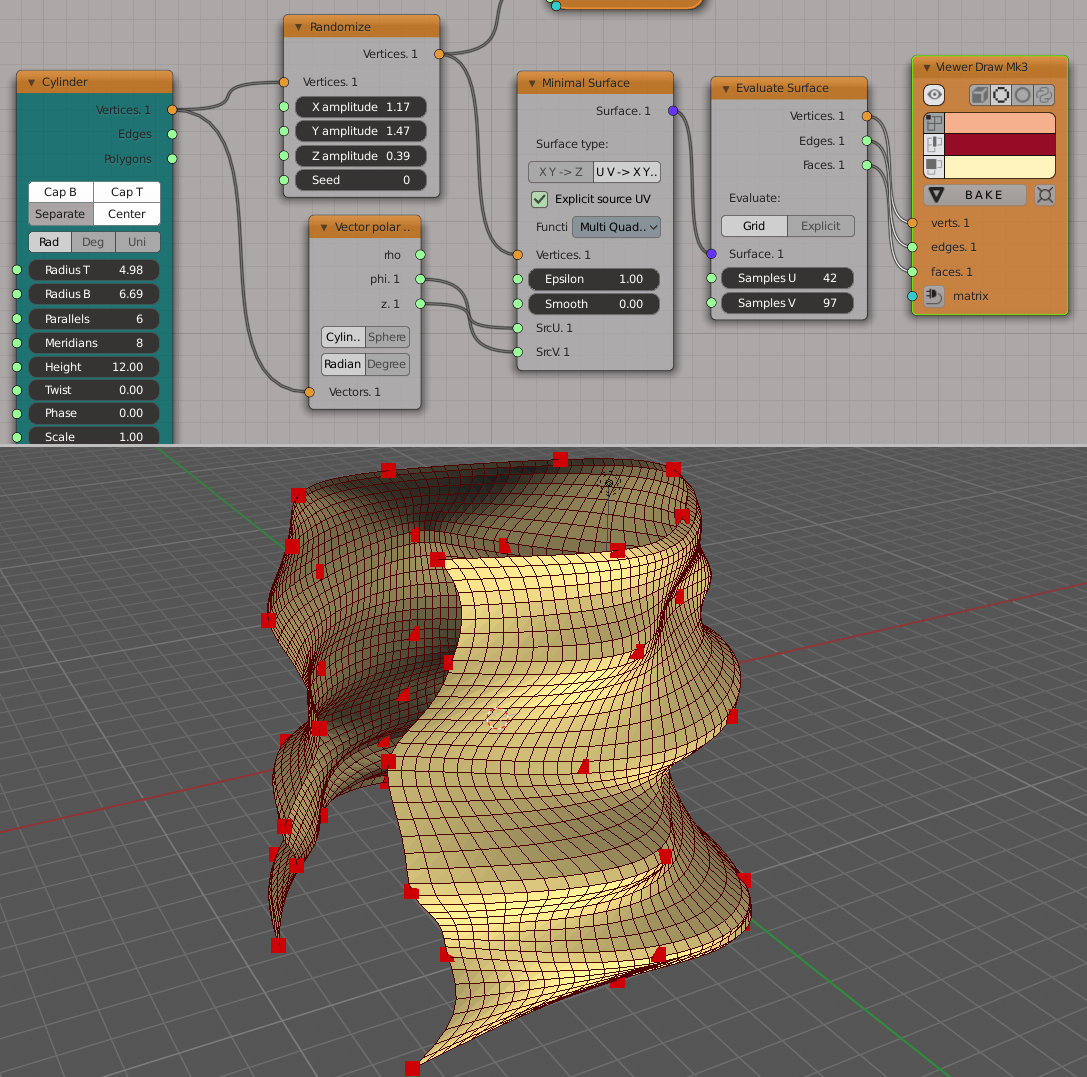
Generator-> Cylinder
Surfaces-> Evaluate Surface
Transform-> Randomize
Vector-> Vector Polar Output
Viz-> Viewer Draw